Network segmentation decreases both performance and security on a network. This conundrum poses a significant challenge for network administrators, as they strive to maintain optimal network performance while ensuring robust security. This article delves into the intricate relationship between network segmentation, performance, and security, exploring the implications and providing practical guidance for balancing these competing demands.
In this comprehensive exploration, we will examine how segmentation affects network performance, including latency, bandwidth utilization, and application responsiveness. We will also analyze the impact of segmentation on network security, considering factors such as attack surface reduction, isolation of compromised devices, and enhanced threat detection.
Network Segmentation: Impacts on Performance and Security: Network Segmentation Decreases Both Performance And Security On A Network.
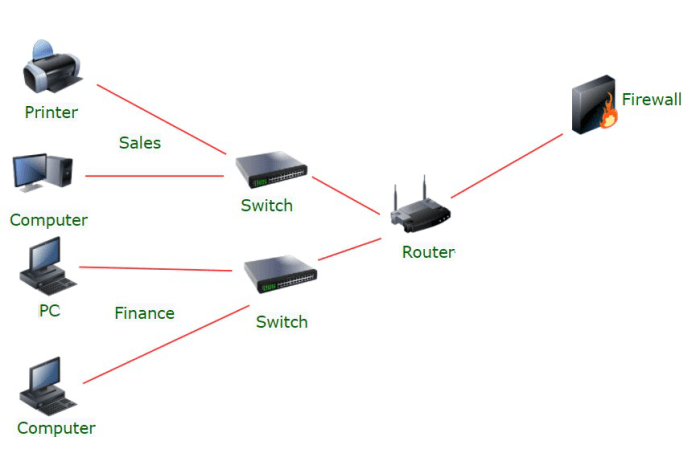
Network Performance
Network segmentation can impact network performance by introducing additional latency and overhead.
Latency:Segmentation divides a network into smaller, isolated segments. This can increase the distance that data must travel between devices, leading to higher latency. Overhead:Segmentation requires additional network infrastructure, such as routers and firewalls, which can consume resources and introduce processing delays.
Mitigation:
- Use high-performance network devices.
- Optimize segmentation design to minimize latency.
- Implement traffic shaping to prioritize critical applications.
Network Security
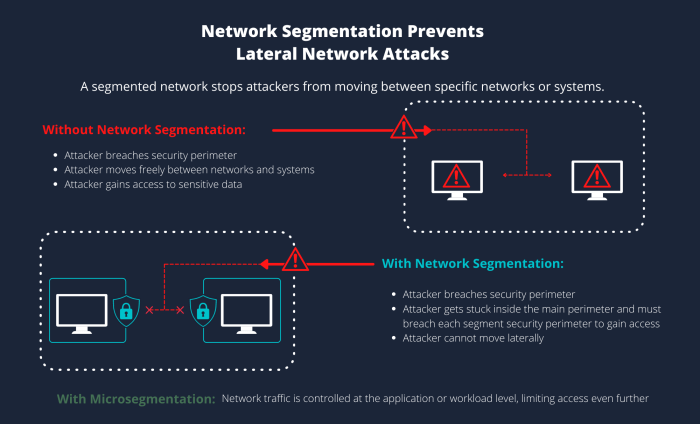
Network segmentation enhances network security by isolating network segments and limiting the spread of threats.
Isolation:Segmentation prevents lateral movement of threats by isolating infected devices or segments from the rest of the network. Limiting Spread:By dividing the network into smaller segments, the potential impact of a security breach is limited to a specific segment, preventing the spread of malware or unauthorized access.
Potential Risks:
- Increased complexity:Segmentation can make network management more complex.
- Misconfiguration:Incorrectly configured segmentation rules can create security vulnerabilities.
Balancing Performance and Security, Network segmentation decreases both performance and security on a network.
| Performance | Security |
|---|---|
| Increased latency and overhead | Enhanced isolation and threat containment |
| Increased complexity | Potential misconfiguration vulnerabilities |
Best Practices:
- Implement segmentation gradually to minimize performance impact.
- Use microsegmentation to isolate specific applications or services.
- Regularly review and optimize segmentation rules.
Decision-Making Flowchart:
- Assess network performance requirements.
- Identify critical applications and data.
- Design segmentation strategy to balance performance and security.
- Implement and monitor segmentation.
Case Studies
Organization A:Implemented microsegmentation to isolate critical applications, resulting in improved security posture without significant performance degradation.
Organization B:Encountered performance issues after implementing segmentation. Resolved by optimizing segmentation design and implementing traffic shaping.
Emerging Trends
Software-Defined Segmentation:Enables dynamic segmentation based on software policies, improving flexibility and scalability.
Zero Trust Segmentation:Assumes all network traffic is untrusted and requires explicit authorization, enhancing security.
FAQ Summary
Does network segmentation always lead to performance degradation?
While segmentation can introduce some performance overhead, it does not necessarily lead to significant degradation. Careful planning, proper implementation, and the use of high-performance networking devices can minimize the impact on performance.
How does network segmentation improve security?
Segmentation isolates different parts of the network, creating smaller attack surfaces and limiting the spread of threats. By confining compromised devices to specific segments, the impact of breaches is contained, preventing attackers from gaining access to the entire network.
What are some best practices for balancing performance and security in segmented networks?
Best practices include using layer 3 switches or routers for segmentation, optimizing firewall rules, implementing traffic shaping, and monitoring network performance metrics to identify and address potential bottlenecks.