A microspectrophotometer measures the pattern of absorption and emission of light by a sample. This information can be used to identify and characterize the sample, as well as to study its structure and function. Microspectrophotometers are used in a wide variety of fields, including biology, chemistry, and materials science.
The first microspectrophotometer was developed in the early 1900s. Since then, the technology has been不斷發展, and microspectrophotometers have become increasingly powerful and versatile. Today, microspectrophotometers are used to study a wide range of samples, from cells and tissues to materials and surfaces.
1. Overview of Microspectrophotometers

Microspectrophotometry is a powerful technique used to measure the pattern of absorbance or emission of light by microscopic samples. It provides detailed information about the chemical composition and structure of materials at the microscopic level.
Types of Microspectrophotometers
- UV-Visible Microspectrophotometers:Measure absorbance in the ultraviolet and visible light range, providing information about the presence of specific molecules.
- Fluorescence Microspectrophotometers:Measure the emission of light from fluorescent molecules, providing information about their concentration and localization.
- Raman Microspectrophotometers:Measure the inelastic scattering of light, providing information about the vibrational modes of molecules.
2. Measurement Techniques
Microspectrophotometry involves the use of a variety of techniques to measure the pattern of absorbance or emission. These include:
- Scanning Microspectrophotometry:Scans a sample across a range of wavelengths, creating a spectrum of absorbance or emission.
- Point Microspectrophotometry:Measures the absorbance or emission at a specific point on a sample.
- Imaging Microspectrophotometry:Creates a map of absorbance or emission across a sample, providing spatial information.
Factors Affecting Accuracy and Precision
The accuracy and precision of microspectrophotometry measurements are affected by factors such as:
- Sample preparation and handling
- Calibration of the instrument
- Signal-to-noise ratio
3. Applications in Biology and Chemistry

Biological Applications
Microspectrophotometry has numerous applications in biological research, including:
- Cell biology:Studying the distribution and localization of molecules within cells.
- Microbiology:Identifying and characterizing microorganisms based on their spectral signatures.
- Biochemistry:Analyzing the structure and function of biomolecules.
Chemical Applications, A microspectrophotometer measures the pattern of
Microspectrophotometry is also used in various fields of chemistry, such as:
- Material science:Characterizing the composition and properties of materials.
- Environmental analysis:Detecting and quantifying pollutants in environmental samples.
4. Data Analysis and Visualization
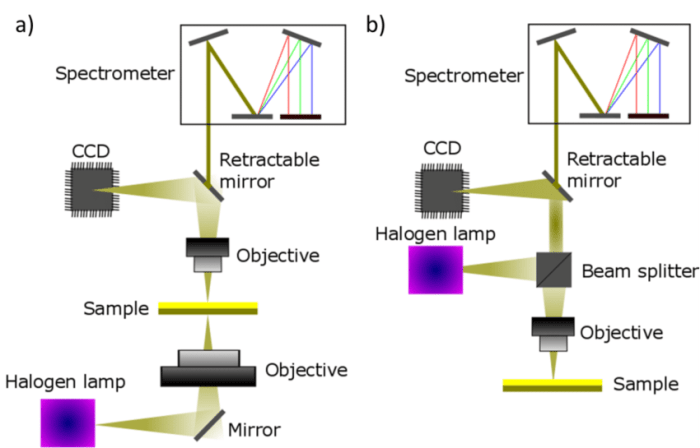
Microspectrophotometry data is typically analyzed using specialized software packages. These packages provide tools for:
- Data preprocessing (e.g., background correction, noise reduction)
- Spectral analysis (e.g., peak identification, curve fitting)
- Data visualization (e.g., spectra, images, scatter plots)
| Software Package | Features |
|---|---|
| OriginPro | Comprehensive data analysis and visualization |
| SpectraSuite | Specialized for microspectrophotometry data analysis |
| MATLAB | Powerful programming environment for custom analysis |
5. Emerging Trends and Future Directions
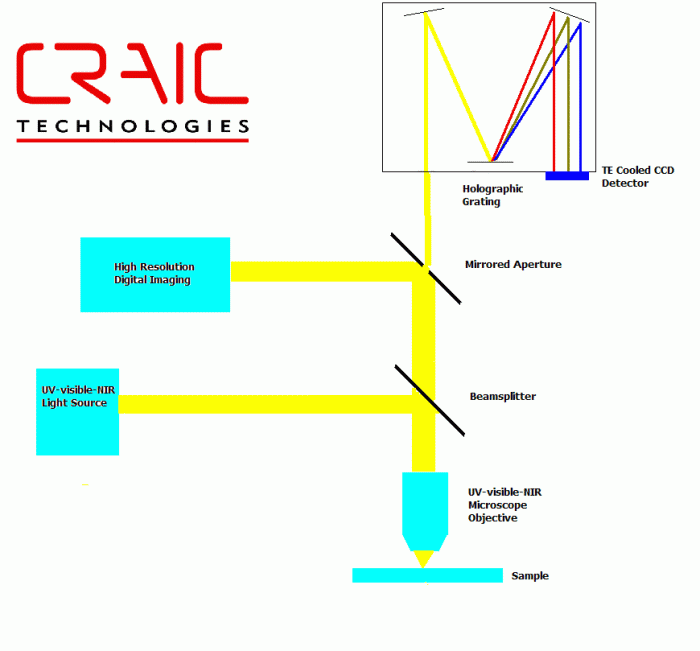
Microspectrophotometry is a rapidly evolving field with several emerging trends and future directions:
- Advancements in instrumentation:Development of new technologies for higher sensitivity, resolution, and speed.
- Multimodal microscopy:Combining microspectrophotometry with other imaging techniques (e.g., fluorescence microscopy, Raman microscopy).
- Machine learning and AI:Application of machine learning algorithms for data analysis and interpretation.
Potential Future Applications
These advancements will open up new possibilities for microspectrophotometry in:
- Medical diagnostics:Early detection and characterization of diseases.
- Drug discovery:Screening and optimization of drug candidates.
- Nanotechnology:Characterization and analysis of nanomaterials.
Quick FAQs: A Microspectrophotometer Measures The Pattern Of
What is a microspectrophotometer?
A microspectrophotometer is a device that measures the absorption and emission of light by a sample.
How does a microspectrophotometer work?
A microspectrophotometer shines a beam of light at a sample and measures the amount of light that is absorbed or emitted by the sample.
What are the applications of microspectrophotometry?
Microspectrophotometry is used in a wide variety of fields, including biology, chemistry, and materials science.